Fiber vs. CO2 vs. UV: Which Laser Machine Is Right for You?
- Redt Inc.
- Dec 9, 2024
- 4 min read
Updated: Dec 30, 2024
| Fiber laser, UV laser , CO2 laser |
When it comes to laser marking, no single solution fits every application.
At Redt Inc., we understand the challenges of finding the right laser technology for your needs. That’s why we’re breaking down the key differences between Fiber, CO2, and UV laser marking machines, helping you make the best decision for your production line.
Why Wavelength Matters
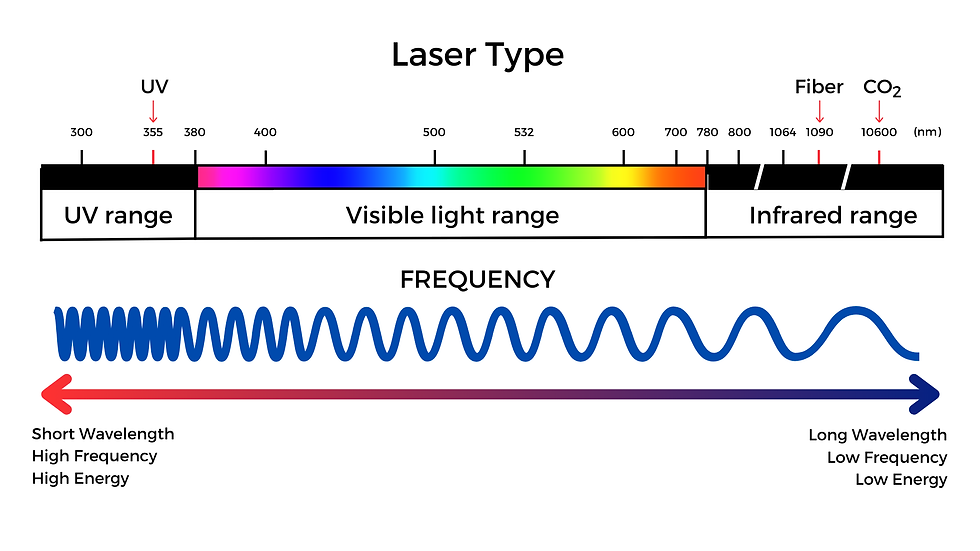
-Laser type and wavelength distribution map-
The core difference between Fiber, CO2, and UV lasers lies in the wavelength of light they emit. Wavelength determines the energy level and absorption rate, directly impacting which materials the laser can mark and the quality of the results.
Laser Type | Wavelength |
UV Laser | 355 nm (short wavelength) |
Fiber Laser | 1090 nm (infrared) |
CO2 Laser | 10,600 nm (far infrared) |
Short wavelengths, like those of UV lasers, offer higher energy and absorption, enabling precision marking on delicate materials. Longer wavelengths, like those of CO2 lasers, are ideal for organic and non-metallic materials.
Understanding Each Laser Type
Fiber Lasers
Fiber lasers operate in the infrared spectrum (1090 nm) and are optimized for metal marking applications.
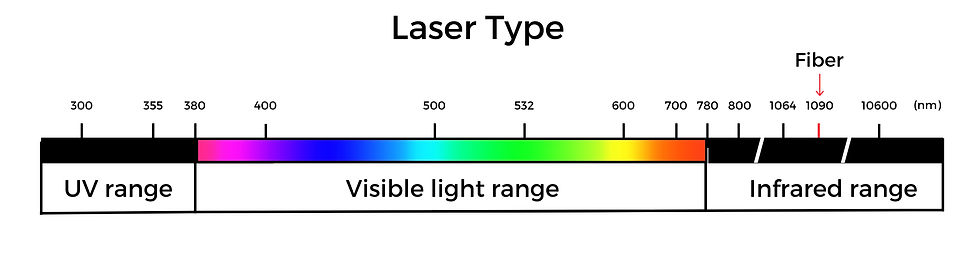
-Light wavelength distribution map-
Their high power makes them excellent for:
- Annealing for high-contrast black marks.
- Engraving on industrial components like engine parts.
- Etching for permanent, durable designs.
However, fiber lasers are less effective on transparent materials, they cannot mark transparent objects since infrared light passes straight through. MAGIC™ fiber laser marking machine is available in 20W, 30W, 60W, and 100W power outputs, giving it the capacity to mark, engrave or cut on a variety of materials like precious metals, steel, stainless-steel, titanium, aluminum, brass, ceramics, plastics, and many others.


MAGIC™-L3
Click below for more
CO2 Lasers
CO2 lasers, with their 10,600 nm wavelength, are perfect for organic and non-metallic materials. CO2 laser machine can easily engrave and cut on wood, acrylic, plastic, anodized aluminum, fabric, leather and many other non-metals.
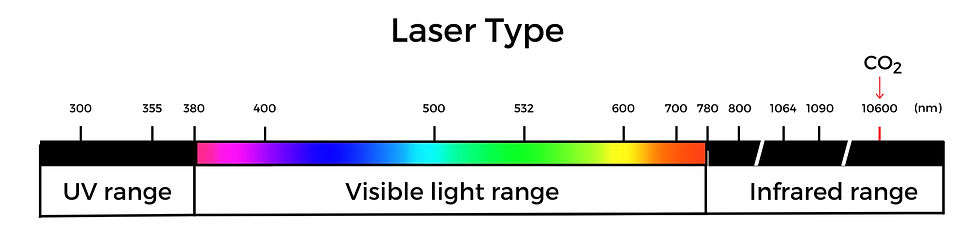
-Light wavelength distribution map-
However, CO2 lasers struggle to mark metals due to poor absorption.


MAGIC™-N5
Click below for more
UV Lasers
UV lasers produce a short wavelength (355 nm) that allows for damage-free marking,
a process often referred to as "cold marking."
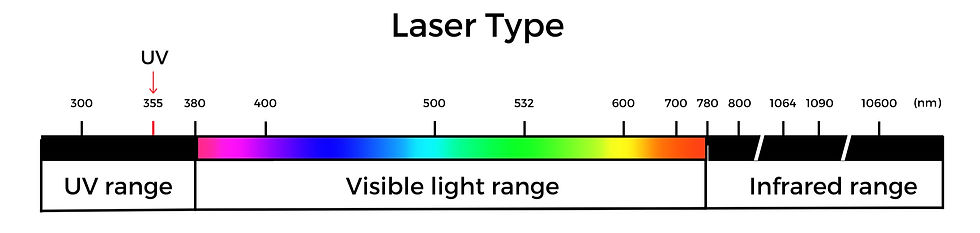
-Light wavelength distribution map-
This precision makes them ideal for:
- High-contrast marking on plastics and resins.
- Applications requiring minimal heat stress, such as medical devices or semiconductors.
Marking cosmetic containers and engraving codes on electronic wafers or medical instruments.


IM™-FUL500
Click below for more
Material Comparison: Fiber vs. CO2 vs. UV
See the difference between Fiber, CO2 and UV laser marks on different materials.
Fiber vs. CO2 vs. UV Marking on Plastic (Resin PE)
Fiber Laser: Highly visible marking is possible, works on dark or treated resins well
CO2 Laser: Highly visible marking is possible,may cause slight melting
UV Laser: Highly visible marking is possible, creates clear, precise markings without damage
Fiber vs. CO2 vs. UV
Marking on Metal
Fiber Laser: Highly visible marking is possible,best for metals, offering deep engraving, high speed, and great contrast.
CO2 Laser: Marking isn't possible because it doesn't absorb CO2 laser light
UV Laser: Highly visible marking is possible
Fiber vs. CO2 vs. UV Marking on Wood
Fiber Laser: Marking isn't possible because wood doesn't absorb fiber laser light
CO2 Laser: Highly visible marking is possible,best for wood, offering deep engraving and fast marking speeds.
UV Laser: Creates fine details but slow and not ideal for deep engraving. (compared to the CO2 laser mark)
Fiber vs. CO2 vs. UV
Marking on Leather
Fiber Laser: Highly visible marking is possible,creates surface discoloration, limited depth.
CO2 Laser: Highly visible marking is possible,best for leather; smooth, fast, and customizable engravings.
UV Laser: Highly visible marking is possible, precise but less efficient for larger areas.
Fiber vs. CO2 vs. UV Marking on Glass
Fiber Laser : Marking isn't possible, low absorption of fiber laser wavelengths (1,064 nm) by glass.
CO2 Laser : Marking isn't possible for detailed work and not reccomended.
UV Laser : Marking is possible, works well on various types of glass, without causing thermal damage or cracks.
Engravable Material Table
Choosing the Right Laser for Your Needs
Selecting the right laser marker depends on your materials, production needs, and desired results. At Redt Inc., we offer tailored solutions to ensure your investment delivers maximum efficiency and quality.
- Fiber Lasers: Best for high-speed, durable metal marking.
- CO2 Lasers: Ideal for organic materials (wood, leather) and bulk processing. Suitable for crafts and large-scale decoration.
- UV Lasers: Perfect for delicate materials requiring precision and minimal heat.
Laser Marking Machines Info
Let Redt Inc. Help You Decide
Every manufacturing process is unique, and choosing the right laser technology is crucial to optimizing your workflow. Whether you need to mark metals, resins, or other materials, Redt Inc. has the expertise and technology to guide you.
Contact us today to discuss your application with our experts.
For further information
Visit our website:
Redt Inc.: https://www.redtinc.com
Email us:
Inquiry: sales@iredt.com
Or, reach us via our social media accounts:
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@RedtInc.
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/magic_engraver
Treads: @magic_engraver


Comments